Revolutionizing Energy: The Transformative Role of IoT in Smart Grid Technology and Applications
1. Aging Traditional Grids:
– Inadequacies of traditional grid systems in meeting growing electricity demands.
2. Global Focus on Smart Grids:
– European Union’s emphasis on sustainable, economic, and secure electricity supplies.
– U.S. government’s decade-long commitment to smart and clean energy policies.
3. Smart Grid Components:
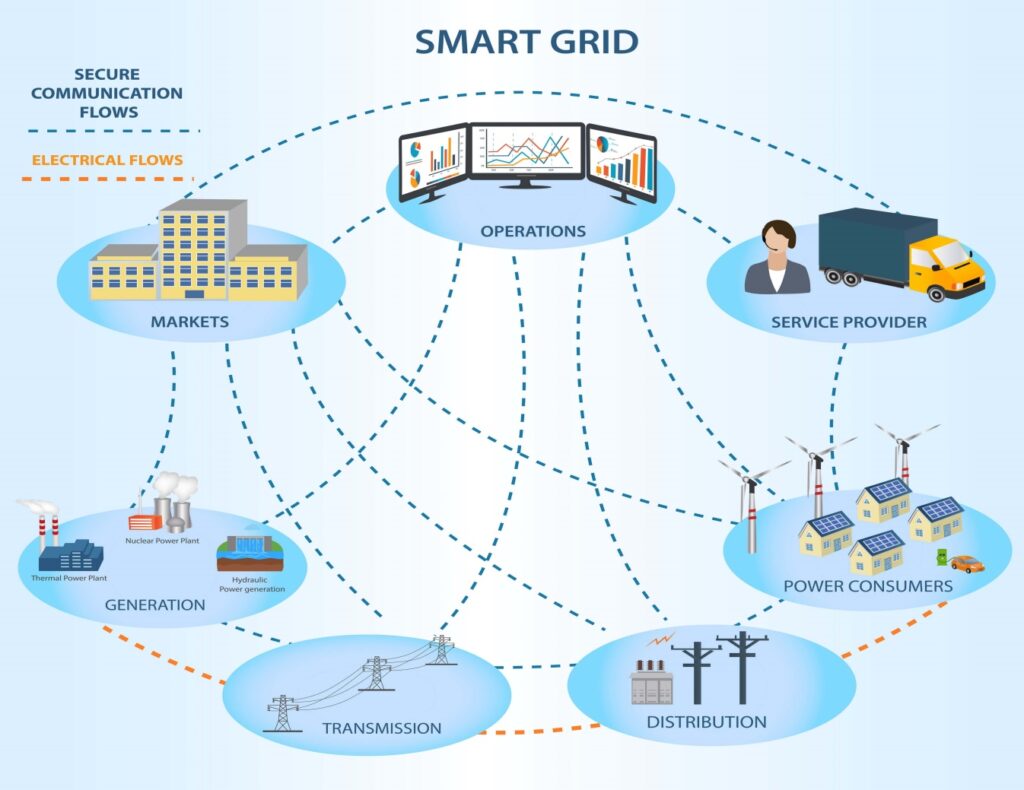
– Electricity network with infrastructural, hardware, and software solutions.
– Facilitates two-way communication for efficient power generation and distribution.
4. Characteristics of Smart Grids:
– Self-sufficient distributed system.
– Capable of utilizing various power sources, including renewables and storage.
– Provides unprecedented control and management capabilities for suppliers and consumers.
5. Complex Network Structure:
– Contrasts one-way communication of traditional grids with the complex, interactive nature of smart grids.
– Enables multiple two-way interactions between equipment and participants in the supply chain.
6. Benefits Over Traditional Grids:
– Demonstrated differences and advantages of smart grids over traditional counterparts.
– Improved efficiency and adaptability to diverse scenarios.
7. Reasons for Smart Grid Adoption:
– Addresses issues like wasted resources and lack of safety in traditional grids.
– Essential for meeting the growing electricity demand in an optimized manner.
8. Household and City Adoption:
– Encourages adoption of smart grid technology at both household and city levels.
– Enables real-time monitoring and control of energy usage.
9. Improved Visibility and Problem Prevention:
– Enhanced visibility of every element in the grid, including loads, equipment, and transmission lines.
– Proactive problem detection to prevent costly issues like outages and downtime.
10. Overall Impact:
– Smart grid technology emerges as a critical solution for the evolving energy landscape.
by Neetu Singh